Many people who are new to the woodworking industry, want to know the differences between CNC machines and laser wood cutting.
In recent years, CNC routers, as well as laser cutters, became very popular tools for beginners. The reason for this comes down to the precision of the machines. Both routers and lasers are computer-controlled along both the X and Y-axis. The use of stepper motors to control the location of the device provided it with an accuracy of less than 1 mm.
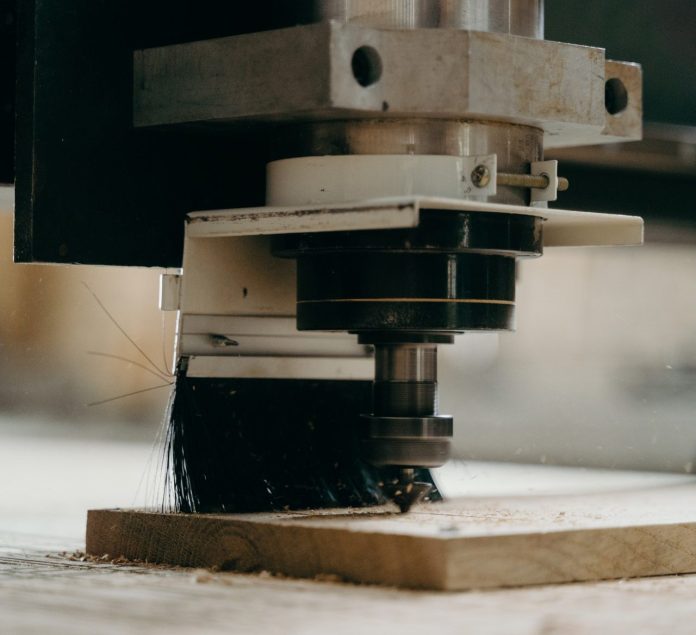
Although subtractive manufacturing uses both machines, there are many differences between them. The routers make use of a spindle head that rotates a tool bit at high speeds to remove material from the workpiece. Lasers, on the other hand, use high-intensity beams of light to remove the material.
CNC Routers and Engravers
The CNC router was one of the first devices available to hobbyists. The original units made use of locally sourced handheld routers. Today, however, they use specially designed spindle heads that mount easily to the Z-Axis and software handles the control.
As these devices use an actual tool bit to remove material from the workpiece, they have the ability to work with a number of popular low-density materials. Common materials used with CNC routers include aluminum, wood, composites, acrylic, and other similar substances. Also, while they engrave on all three axes with a high level of precision, you must consider the width of the bit used to cut the material.
CNC Cutting’s Benefits
Dedicated CNC wood cutting services have many benefits that make them a popular choice amongst woodworkers. For starters, their use does not require a lot of skill or training. Therefore, just about anyone has the ability to operate them. Additionally, thanks to readily available software, the tool paths used by the CNC to cut and engrave program with relative ease. Once programmed, the operator only has to set up the work area, then sit back and monitor the progress. As a result, a single operator very easily watches multiple machines work at the same time.
Application of CNC Cutting
Today, a wide variety of applications use CNC cutters and routers. Sign making is one of the most common industries where one finds these devices. Although popular throughout the woodworking industry, the use of a CNC router is generally limited to cabinetmaking and other similar forms of carpentry. Additionally, plastic fabrication as well as stitch and glue boat construction use them.
Laser Cutters and Engravers
Unlike CNC machines, laser cutters and engravers come in two main forms. Low-end units feature a laser diode, while the higher-end models use a CO2 laser. While a CNC router has a Z-axis, laser cutters rely on the adjustment of the power and focal point to change the depth of the cut. Today, a number of manufacturers produce laser diode units capable of cutting wood up to three-quarters of an inch thick.
Because these devices use a beam of light to remove material from the workpiece, they have limitations on the number of low-density materials used. For example, while they are great for cutting black pigmented acrylic, most laser diodes have issues cutting into blue pigmented and clear acrylic. With that said, unlike a CNC router, most laser engravers feature a beam that is finer than 1/10 of a millimeter in diameter. As a result, a laser cutter or engraver provides more precise cuts.
Laser Wood Cutting’s Benefits
When it comes to precise cuts, nothing beats the capability of a laser cutter. The device itself uses a beam of light to remove material from the workpiece. As such, the more focused that beam of light is, the better it is at removing material. For most laser-powered devices, this results in a precise incision of less than 1/10 of a millimeter in width.
Laser engravers have many benefits over a CNC router. The biggest of these is the ability to effectively burn a two-dimensional image onto a workpiece. By varying the intensity of light being projected onto the workpiece, the machine adjusts the depth of its cuts. More importantly, because this is a no-contact form of processing, there is less stress on the actual machine as it cuts into the workpiece.
Application of Laser Cutting
Sign making, for the most part, uses laser cutters. And although the more expensive CO2-powered devices are utilized for a large variety of purposes, laser diode devices are more common and readily available. Laser engravers are the common choice because of their precision to reproduce intricate parts such. These parts include wooden puzzles and invitations, as well as decorations such as emblems and ornaments.
The Major Differences Between CNC Machine and Laser Wood Cutting
The main difference between a CNC router and a laser engraver is the way the material removes from the workpiece. While the CNC cutter requires continuous contact with the workpiece, a laser cutter does not.
Cut and Engraving Quality
The diameter of a laser is so small that it allows the device to produce a product of higher quality than one achieved with a router. Routers need to contact the material worked on, which results in a drag on the system. This in turn sometimes leads to issues with the engraving resolution. However, the way in which a laser engraver operates leaves scorch marks in the manufacturing process.
Cut and Engraving Depth
The focal length of the lens limits a laser cutter. As a result, most laser cutters are unable to cut more than three-quarters of an inch into a piece of wood. While a CO2 laser is much more efficient at this type of cutting, newer versions of dual diode lasers accomplish the same feat. A CNC router, on the other hand, has limits to the length of the cutting bit, and the travel of the Z-axis. As a result, CNC routers cut deeper into a larger variety of materials.
Material Preparation
When it comes to material preparation, there are a few factors to consider. For starters, a laser engraver does not require that the workpiece is perfectly flat, while a CNC router does. Next, because a CNC router contacts the material worked on, the material has to be secured down to the cutting table. As a result, a laser engraver requires a lot less material preparation than a router does.
Life Expectancy
Both CNC spindles as well as laser tubes and diodes have limited life expectancy. CO2 lasers have the shortest life expectancy and require replacement on a regular basis. The spindles used for CNC routers receive excessive lateral forces which wear down the equipment and bearings. As a result, a CNC spindle lasts longer than a CO2 laser, but not nearly as long as a diode laser. A diode laser’s life expectancy is based on the number of hours they are in operation. Since most diodes last about 35,000 hours, with proper maintenance, laser wood cutting modules last five years or more.
Environmental Factors
We also must consider environmental factors. CNC routers produce a lot of dust, and that dust needs to be collected and disposed of properly. Luckily, the dust produced by routers recycles making it more environmentally friendly. A laser engraver on the other hand effectively burns through the material. As a result of this process, toxic gasses release into the work area. Therefore, proper ventilation is necessary to work with common materials such as plywood and acrylic.
Costs and Savings
As always, cost and savings are some of the most important factors when it comes to choosing any piece of equipment. Because of their simplicity, CNC routers cost substantially less than a CO2 laser. However, thanks to many great advances in technology, dual diode laser engravers became the most affordable option. However, because of the higher power consumption of laser-powered devices, they end up costing more in the long run.
Find a Home-Based Business to Start-Up >>> Hundreds of Business Listings.