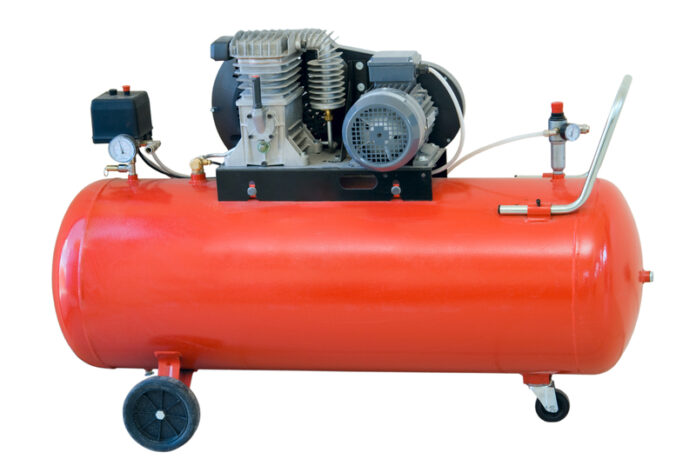
An air compressor is a valuable asset, whether you’re a weekend DIYer powering nail guns or a professional relying on pneumatic tools for your livelihood. Like any piece of machinery, however, it requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance, extend its lifespan, and prevent costly breakdowns. Neglecting basic upkeep can lead to reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, and ultimately, the need for premature replacement. This guide will walk you through essential air compressor maintenance practices, providing you with the knowledge to keep your unit running smoothly and reliably for years to come. Even if you sourced your unit from a dependable air compressor supplier, consistent maintenance remains key.
Why Regular Maintenance Matters: Protecting Your Investment
Investing in an air compressor is a significant outlay, and proper maintenance is the most effective way to protect that investment. Regular upkeep not only ensures peak performance and efficiency but also helps to identify potential issues early on, preventing minor problems from escalating into major repairs. Think of it as preventative medicine for your machinery – a little attention now can save you significant headaches and expenses down the line.
The Cornerstone of Compressor Care: Draining the Tank Regularly
One of the most fundamental air compressor maintenance tasks for any air compressor is draining the air tank. As the compressor operates, moisture in the air condenses inside the tank. If this moisture is not regularly drained, it can lead to rust and corrosion, weakening the tank over time and potentially causing leaks or even catastrophic failure. Water buildup also reduces the effective air storage capacity of the tank.
How and When to Drain Your Air Compressor Tank
The frequency of draining depends on the humidity levels in your environment and how often you use your compressor. As a general rule, drain the tank after each use, especially if you’ve been running the compressor for an extended period. Most compressors have a drain valve located at the bottom of the tank. Place a container beneath the valve and slowly open it to release the accumulated water and air pressure. Ensure the compressor is turned off and disconnected from the power source before draining.
Keeping Things Clean: The Importance of Air Filter Maintenance
The air intake filter prevents dust, debris, and other contaminants from entering the compressor pump. A clogged or dirty air filter restricts airflow, forcing the motor to work harder, reducing efficiency, and potentially causing overheating and damage.
Refer to your compressor’s manual for the location and type of air filter it uses. Some filters are washable; these can typically be cleaned with compressed air or mild soapy water, ensuring they are completely dry before reinstallation. Other filters are disposable and need to be replaced periodically according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Inspect the air filter regularly and clean or replace it as needed to maintain optimal airflow.
Oil is the Lifeblood: Checking and Changing Compressor Oil (for oil-lubricated models)
Many reciprocating air compressors utilize oil for lubrication, reducing friction and wear on internal components. Air compressor maintenance means having the correct oil level. Additionally, changing the oil at the recommended intervals is crucial for the longevity of these models.
Locate the oil sight glass or dipstick on your compressor and check the oil level regularly, ideally before each use. The oil level should be within the indicated range. Use only the type and viscosity of oil recommended by the manufacturer. Over time, oil degrades and loses its lubricating properties, so follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for oil change intervals. This often involves draining the old oil and refilling with fresh oil to the correct level.
Belt Inspection and Adjustment (for belt-driven models)
Some air compressors, particularly larger models, use a belt to transfer power from the motor to the pump. A loose or worn belt can slip, reducing efficiency and potentially causing damage to the belt or pulleys.
Air compressor maintenance means regularly inspecting the belt for signs of wear, cracks, or fraying. Ensure the belt has the correct tension; it should have a slight amount of play but should not be excessively loose or tight. Refer to your compressor’s manual for the proper belt tensioning procedure. Adjust the tension as needed by loosening the motor mount and repositioning the motor. Replace worn belts promptly.
Checking for Air Leaks: Preventing Wasted Energy
Air leaks not only reduce the efficiency of your compressor but also force it to run more frequently, increasing energy consumption and wear and tear. Regularly inspect all hoses, fittings, and connections for air leaks.
One way to check for leaks is to listen for hissing sounds when the compressor is running or pressurized. You can also apply soapy water to connections; bubbles will form where there is a leak. Tighten any loose fittings. Replace damaged hoses or fittings as necessary. Addressing leaks promptly can save you money on energy bills and prolong the life of your compressor.
Maintaining Proper Lubrication (for oil-free models)
While oil-free compressors eliminate the need for oil changes, they still require some level of lubrication. Internal components in these models are often pre-lubricated or utilize specialized materials.
Refer to your compressor’s manual for specific maintenance recommendations for oil-free models. This might include periodic inspection and replacement of seals or other internal components. While less frequent than oil changes, these tasks are still important for maintaining the performance and lifespan of your oil-free compressor.
Electrical Connection Checks: Ensuring Safety and Reliability
Regularly inspect the electrical cord, plug, and connections for any signs of damage, such as fraying or loose wires. Damaged electrical components can pose a safety hazard and lead to unreliable operation.
Ensure the power cord is in good condition and properly grounded. Avoid using extension cords unless absolutely necessary and ensure they are of the appropriate gauge for the compressor’s power requirements. If you notice any damage to the electrical components, have them inspected and repaired by a qualified electrician.
Cleaning the Compressor Exterior: Preventing Overheating
Dust and debris can accumulate on the exterior of the compressor, hindering proper cooling and potentially leading to overheating.
Air compressor maintenance means periodically wipe down the exterior of your compressor with a clean, dry cloth to remove dust and debris. Ensure the cooling vents are not obstructed. Proper ventilation is essential for preventing the motor from overheating.
Tightening Fasteners: Preventing Vibration Issues
Over time, vibrations from the compressor’s operation can cause fasteners like bolts and screws to loosen. Regularly check and tighten any loose fasteners to prevent excessive vibration and potential damage.
When to Seek Professional Help: Recognizing Limitations
While many basic maintenance tasks can be performed by the owner, some repairs and more complex issues require the expertise of a qualified technician. Don’t hesitate to contact a reputable service center or the air compressor supplier for assistance when needed. Attempting repairs beyond your skill level can lead to further damage or safety hazards.
The Long-Term Benefits of Consistent Air Compressor Maintenance
Investing a little time and effort in regular air compressor maintenance will pay significant dividends in the long run. You’ll enjoy more consistent performance, extend the lifespan of your unit, reduce the risk of unexpected breakdowns, and potentially save money on energy costs and repairs. Even the most robust compressors rotary screw designs benefit from diligent upkeep.
Conclusion
Air compressor maintenance is not a complex or time-consuming endeavor, but it is a crucial aspect of ownership. By following these essential tips, from regularly draining the tank and maintaining the air filter to checking oil levels and inspecting for leaks, you can ensure your air compressor continues to run smoothly and reliably for years to come, providing the power you need for all your projects.
Find a Home-Based Business to Start-Up >>> Hundreds of Business Listings.