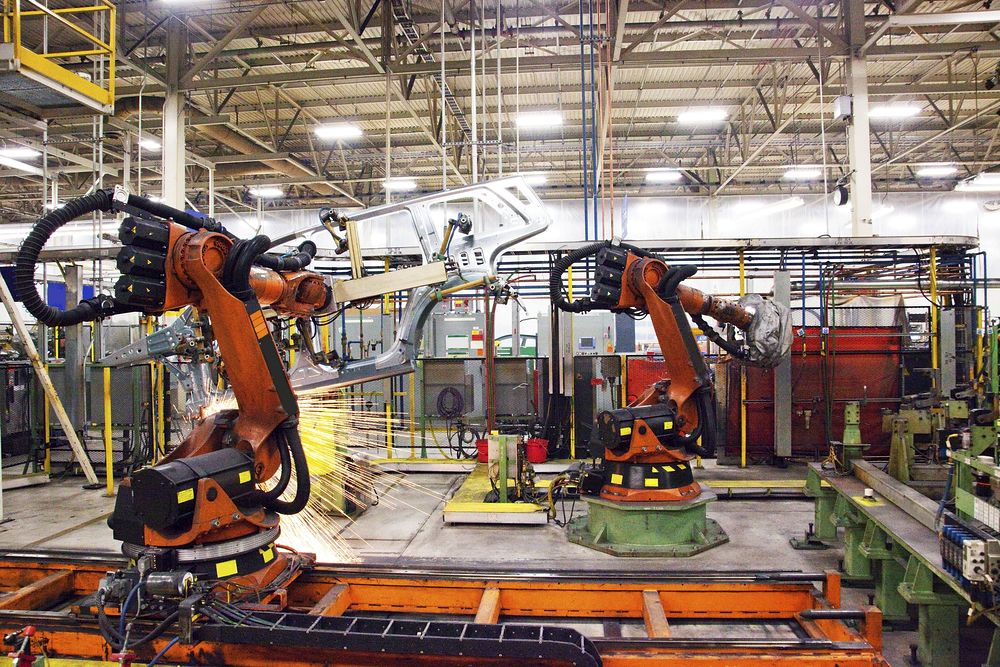
Motion control, a fundamental component of modern automation systems, orchestrates the movement of machines with exceptional precision. Its integration into various industries has transformed operational efficiencies, enhancing productivity and safety while reducing costs. This article delves into the intricacies of motion control, illustrating its role and benefits in automation.
What is Motion Control?
Motion control manages and directs the movement of machine parts through controlled systems that include motors and actuators. Essentially, it is the brain behind the motion in automated machinery, ensuring actions are smooth, precise, and efficient. By regulating speed, position, and torque, motion control systems are pivotal in complex manufacturing and assembly processes.
Basic Principles of Motion Control
At its core, motion control involves three primary elements:
- Positioning: Determining the position of a machine part accurately.
- Velocity: Managing the speed at which parts move.
- Torque: Controlling the force that drives the motion.
These principles are executed through a combination of hardware and software components, creating a system that can repetitively achieve exact movements with minimal error.
How Does Motion Control Work in Automation?
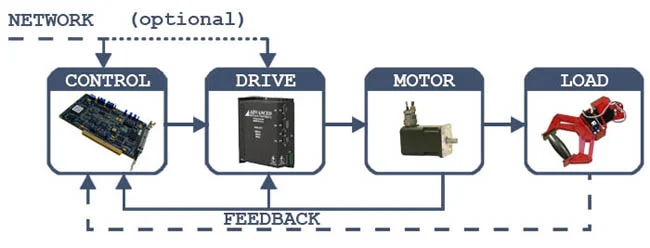
A typical motion control system comprises several key components, each serving a unique function in achieving precise and controlled motion.
- Controllers: The central processing units that issue commands to the machine.
- Servo Drives: These convert the controller’s command signals into higher-power electrical currents to drive the motors. ADVANCED Motion Controls servo drives emphasize the importance of specialized knowledge and years of experience in manufacturing. Renowned for providing cutting-edge solutions, the company has established a solid reputation and become a standard-setter in the industry.
- Motors: Act as the actuators that induce the actual motion.
- Feedback Devices: Sensors that provide real-time data back to the controller to ensure movements adhere to the set parameters.
- Software: Programs that facilitate communication and operation among all components.
These components integrate seamlessly to form a system capable of executing complex and precise movements essential for modern automation.
What are the Benefits of Motion Control in Automation?
The adoption of motion control systems brings numerous advantages:
- Precision and Accuracy: Ensures tasks are performed with exactitude, crucial in applications like CNC machining, and robotic surgery.
- Increased Productivity: Automates repetitive tasks, speeding up production cycles.
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces the need for manual intervention, lowering the risk of accidents.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizes power use, reducing operational costs.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Adapts easily to different tasks and can be scaled up or down based on demand.
What are the Different Types of Motion Control Systems?
Motion control systems vary widely, each suited to particular applications based on their operational needs.
Open-Loop Motion Control Systems
These systems operate without feedback, suitable for simple, less critical tasks where precision is less of a concern. Their simplicity makes them cost-effective, though they lack the ability to correct errors in real-time.
Closed-Loop Motion Control Systems
In contrast, closed-loop systems use feedback to continuously adjust and correct the motion, essential in applications requiring high precision and reliability. While more complex and costly, they provide significant advantages in critical tasks.
Linear Motion Control Systems
These are designed to deliver movement in a straight line and are fundamental in assembly lines and 3D printing.
Rotary Motion Control Systems
These systems provide rotational motion and are crucial in applications like robotic arms and wind turbines.
What are the Main Components of a Motion Control System?
Detailed below are the essential parts of a motion control system:
- Controllers
- Drives
- Motors
- Feedback Devices
- Software
These components are the building blocks of any motion control system, each playing a critical role in ensuring its effective operation.
How to Choose the Right Motion Control System for Your Application?
Selecting an appropriate motion control system requires consideration of several factors:
- Application Requirements: Understanding the specific needs of your application.
- Precision and Accuracy Needs: Determining how precise the system needs to be.
- Environmental Conditions: Considering factors like temperature and humidity which can affect system performance.
- Budget Constraints: Balancing cost against system capabilities.
- Compatibility with Existing Systems: Ensuring new components integrate smoothly with current setups.
What are the Applications of Motion Control in Automation?
Motion control systems find applications across various industries, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Manufacturing
Specific uses in manufacturing include:
- Assembly Lines: Streamlining the assembly process.
- CNC Machines: Enhancing precision in different types of CNC machining.
Robotics
In robotics, motion control is fundamental in enabling precise movements and tasks.
Packaging
Streamlines the packaging process, improving speed and efficiency.
Automotive
Crucial for automated processes in vehicle manufacturing.
Aerospace
Ensures the precise assembly of highly sensitive aerospace components.
Medical Devices
Facilitates the manufacture of intricate medical devices like pacemakers.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
Essential in the production of semiconductors, where precision is critical.
What are the Key Technologies in Motion Control?
Key technologies include:
Servo Motors
Servo motors provide precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration.
Stepper Motors
Stepper motors are essential for applications requiring precise positioning and repeatability.
Encoders
Used to provide feedback on position and speed to the motion controller.
PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers)
Manage the hardware components and execute the control software.
HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces)
Allow operators to interact with the motion control system, adjusting parameters and monitoring system status.
How to Implement Motion Control in an Automation System?
Implementing motion control involves several steps:
- Assessment and Planning: Evaluating the specific needs and challenges of the intended application.
- Selection of Components: Choosing appropriate technologies and components.
- System Integration: Combining all components into a cohesive system.
- Testing and Validation: Ensuring the system meets all specifications and operational requirements.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Establishing routines for regular upkeep and resolving issues as they arise.
What are the Challenges in Motion Control for Automation?
Key challenges include:
- System Complexity: Ensuring all components work harmoniously.
- Integration Issues: Seamlessly integrating new technologies with existing systems.
- Maintenance and Reliability: Keeping the system running reliably over time.
- Cost Considerations: Balancing cost with system capabilities and needs.
- Training and Skill Requirements: Ensuring staff are adequately trained to operate and maintain the system.
How Does Motion Control Improve Manufacturing Efficiency?
Motion control significantly enhances manufacturing efficiency by:
- Reducing Cycle Times: Faster production rates are achieved by streamlining processes.
- Improving Product Quality: Consistent production methods lead to higher quality products.
- Minimization of Waste: Precision in production minimizes material waste.
- Better Resource Utilization: Efficient processes use resources more effectively.
What are the Safety Considerations for Motion Control Systems?
Important safety tips include:
- Proper Training for Operators: Ensuring all operators are trained on the system.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Keeping the system in optimal condition.
- Emergency Stop Mechanisms: Incorporating safety features to halt the system immediately if needed.
- Use of Safety Guards and Barriers: Protecting workers from moving parts.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Adhering to all relevant safety standards.
How to Maintain and Troubleshoot Motion Control Systems?
Maintenance and troubleshooting tips:
- Regular Inspections: Routine checks to ensure all components function correctly.
- Firmware and Software Updates: Keeping software up to date to ensure system security and functionality.
- Calibration of Sensors and Encoders: Regular calibration to maintain accuracy.
- Lubrication of Moving Parts: Essential for smooth operation.
- Keeping the Environment Clean and Dust-Free: Ensures components remain in good working condition.
What are the Future Trends in Motion Control and Automation?
Emerging trends include:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Enhancing predictive maintenance and system optimization.
- IoT and Industry 4.0: Connecting devices and systems for improved data analytics and system management.
- Advanced Robotics: Developing more sophisticated robots that can perform complex tasks autonomously.
- Improved Human-Machine Collaboration: Creating systems that enhance the interaction between humans and machines.
Conclusion
Motion control is pivotal in modern automation, driving advancements across various industries. Its ability to enhance precision, efficiency, and safety while reducing costs makes it an indispensable component of contemporary manufacturing and production processes. As technology evolves, the role of motion control is set to become even more integral, ushering in new possibilities for automation and efficiency.
Find a Home-Based Business to Start-Up >>> Hundreds of Business Listings.