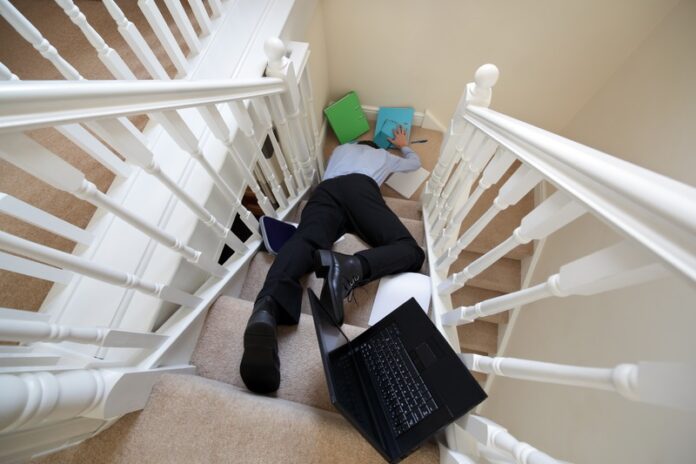
Workplace injuries are a significant concern for both employees and employers, often leading to downtime, financial costs, and legal obligations. When an injury occurs, it is crucial for employers to respond promptly and fulfill their responsibilities to protect both the injured employee and the company. Understanding what is required from a legal, ethical, and practical standpoint can help business owners navigate these situations effectively and reduce the risk of future incidents.
Immediate Response to the Injury
The first responsibility of an employer after a work injury is to ensure that the injured employee receives the necessary medical attention. Depending on the severity of the injury, this could mean administering first aid on-site or contacting emergency services to take the employee to a medical facility. In less severe cases, employers should direct the employee to a healthcare provider who is familiar with work-related injuries.
Employers should also ensure that the incident scene is secure, preventing further injuries to other employees. This includes removing or isolating any dangerous equipment, fixing hazards, or closing off unsafe areas of the workplace.
Reporting the Injury
Once the injured employee has received medical care, employers are required to report the injury to their workers’ compensation insurance carrier. An experienced injury attorney in Los Angeles explains that in most jurisdictions, businesses have a legal obligation to report workplace injuries, even if they seem minor at first. Failing to report injuries can result in penalties and may also limit the employer’s ability to defend against future claims.
In addition to internal reporting, depending on the severity of the injury, employers may be required to notify local or national regulatory agencies, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States. These organizations often require injury reports for certain types of incidents, particularly those involving hospitalization, amputation, or fatalities.
Investigating the Incident
Employers must conduct a thorough investigation of the injury to determine its cause and prevent similar incidents in the future. This involves interviewing the injured employee (if possible), coworkers who may have witnessed the event, and reviewing any video footage or safety logs. The goal of the investigation should not be to assign blame but to identify what went wrong and how safety protocols can be improved.
Proper documentation of the investigation is essential. Employers should create a detailed report that includes the time and date of the incident, a description of the injury, witness statements, and any corrective actions taken as a result of the investigation. Keeping accurate records will also protect the company in case of future legal claims.
Filing a Workers’ Compensation Claim
Employers are generally required to file a workers’ compensation claim on behalf of the injured employee. Workers’ compensation provides financial support for medical bills and lost wages, allowing the injured worker to recover without the financial strain. It also protects employers from lawsuits, as employees typically cannot sue their employer if they receive workers’ compensation benefits.
The claim process requires employers to submit necessary documentation to the insurance company, including the details of the injury, the medical diagnosis, and any reports from the investigation. Timely submission is critical since delays can lead to complications in the claims process and could result in fines or legal repercussions.
Supporting the Employee’s Recovery and Return to Work
Another key responsibility of employers is to support the injured employee throughout their recovery. This includes maintaining communication with the employee to check on their progress and ensuring they have access to the appropriate medical care. In many cases, the employer may need to coordinate with healthcare providers to assess the employee’s ability to return to work, either in a full or limited capacity.
If the employee is unable to return to their previous role due to long-term effects from the injury, employers may need to explore accommodations under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) or similar regulations, depending on the jurisdiction. This could involve modifying the employee’s duties, providing assistive equipment, or offering alternative work positions.
Preventing Future Injuries
One of the most important outcomes of handling a workplace injury is the opportunity to improve safety protocols to prevent future incidents. Employers are responsible for reviewing their workplace safety programs and ensuring that they meet regulatory standards. If gaps in safety measures contributed to the injury, employers must take corrective actions such as updating safety training, revising procedures, or improving equipment.
Providing ongoing safety training and fostering a culture of safety in the workplace can significantly reduce the risk of injuries. Employees should feel empowered to report potential hazards and take proactive steps to keep their environment safe.
Legal Compliance and Recordkeeping
Employers must stay compliant with legal requirements related to workplace injuries, which includes maintaining accurate records of all work-related injuries and illnesses. In the U.S., OSHA requires many employers to keep injury and illness records, typically through an OSHA 300 log. These records must be maintained for a specific period and may be subject to audits or inspections.
Additionally, businesses should stay informed about any changes to workers’ compensation laws or safety regulations that could affect their responsibilities after a workplace injury. Consulting with legal or safety experts can help ensure ongoing compliance and reduce the risk of legal complications.
When a workplace injury occurs, employers have several critical responsibilities—from providing immediate medical care to investigating the incident and supporting the injured employee’s recovery. Fulfilling these obligations not only helps protect the injured worker but also ensures the business remains compliant with legal and safety standards. By taking proactive steps to improve workplace safety, employers can create a safer environment for their employees and minimize the likelihood of future injuries.
Find a Home-Based Business to Start-Up >>> Hundreds of Business Listings.