Companies and governments issue bonds as a kind of debt security to raise money. When you purchase a bond, you are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for a fixed rate of return, known as the coupon rate, over a set period of time. The coupon rate is the amount of interest that the bond pays to the bondholder on an annual basis. The bond also has a face value, also known as the par value, which is the amount the bond will be worth when it matures.
When an issuer wants to raise capital, they issue bonds to investors in exchange for money. The issuer is then obligated to make regular interest payments to bondholders, and return the principal amount of the bond when it matures. Bond investments can be a wonderful method to reduce risk and diversify your investment. Because bonds have a fixed rate of return, they can provide a steady stream of income for investors.
Understanding Bond Basics
Before you start trading bonds, it’s important to understand some of the basic concepts. A bond is essentially a loan that an investor makes to a company or government. The bond issuer promises to pay the investor a fixed rate of interest over a set period of time and to return the principal amount at maturity. The interest rate is known as the coupon rate, and the maturity date is the date on which the bond issuer must return the principal to the investor.
Bonds are typically rated by credit rating agencies, such as Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s, to indicate the level of risk associated with the bond. The risk and interest rate is lower when the rating is high.
How to Trade Bonds
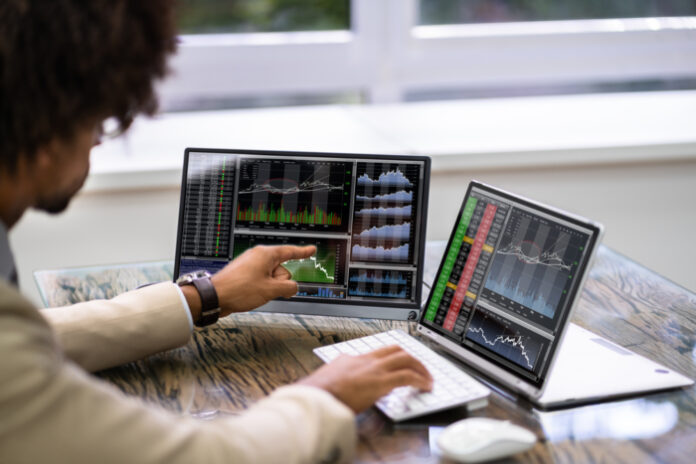
Bonds can be traded through a variety of channels, including brokerage firms, banks, and online platforms. One option is to trade government bonds with help of forex brokers. Forex brokers often provide access to government bonds, and they can provide valuable research and analysis to help you make informed decisions.
When trading bonds, it’s important to consider factors such as the creditworthiness of the issuer, the coupon rate, and the maturity date. You should also be aware of the impact of interest rate changes on bond prices, as rising interest rates can cause bond prices to fall.
Types of Bonds
There are several different types of bonds available for investors to choose from. Some of the most common include:
-
Government Bonds
These bonds are issued by national governments and are considered to be among the safest investments. They typically offer lower returns than other types of bonds, but they also carry less risk.
-
Corporate Bonds
Companies issue these bonds to raise revenue. They offer higher returns than government bonds, but they also carry more risk. The creditworthiness of the company issuing the bond is a key factor to consider when evaluating corporate bonds.
-
Municipal Bonds
These bonds are issued by state and local governments to finance infrastructure projects. They are generally considered to be less risky than corporate bonds, but they may be subject to state and local taxes.
-
Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS)
These U.S. government-issued bonds are intended to shield investors from inflation. The interest rate and principal value of these bonds are adjusted for inflation, making them an attractive option for investors looking for a hedge against rising prices.
How to Evaluate Bonds
When evaluating bonds, it’s important to consider the following factors:
-
Creditworthiness of the Issuer
This refers to the ability of the bond issuer to pay the interest and principal on the bond. Credit ratings from agencies like Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s can provide a useful indication of the risk associated with a bond.
-
Coupon Rate
This is the interest rate paid to bondholders. A higher coupon rate generally indicates a higher return, but it also means that the bond is less sensitive to changes in interest rates.
-
Maturity Date
This is the date on which the bond issuer must return the principal to the investor. Longer-term bonds offer higher coupon rates, but they also carry more interest rate risk.
-
Market Conditions
The bond market can be affected by a variety of factors, including changes in interest rates, economic conditions, and political events. It’s important to stay informed about current market conditions and how they may impact bond prices.
Conclusion
Bond investments can be a brilliant strategy to diversify your investment and generate a consistent income. With knowledge of bond basics, types of bonds, how to evaluate creditworthiness, bond funds, investors can make informed decisions and potentially earn a steady stream of income from their investments.
FAQ:
Q: What is the bond’s coupon rate?
A. The coupon rate is the amount of interest that the bond pays to the bondholder on an annual basis. Its proportion of the bond’s face value is how it is expressed.
Q: What is the face value or par value of a bond?
A. The face value, also known as the par value, is the amount the bond will be worth when it matures.
Q: How are bonds different from stocks?
A. Bonds and stocks are both securities, but they represent different types of investments. Bonds represent a debt to a corporation or government, whereas stocks indicate ownership in a company.
Q: How long should I hold bonds?
A. The length of time you should hold a bond depends on your investment goals and risk tolerance. Generally, short-term bonds are less risky than long-term bonds, but they also tend to have lower yields. Long-term bonds can offer higher yields, but they are also more sensitive to interest rate changes.
Find a Home-Based Business to Start-Up >>> Hundreds of Business Listings.